Fainting is abrupt, brief loss of consciousness that results in a fall. In most instances, when an individual faint, he/she will regain consciousness in 1-2 minutes. Nevertheless, the uncommon forms of fainting can be considered as medical emergencies. Call for an ambulance if an individual who fainted does not regain consciousness within 2 minutes.
What are the causes?
For the brain to function properly, it depends on the oxygen transported by the blood. Fainting can occur if the flow of blood to the brain is reduced. The body typically corrects the poor blood flow to the brain rapidly, but it can make the individual sweat and dizzy. If it lasts for some time, the individual might faint.
There are various reasons for a poor flow of blood to the brain, but it is usually linked to a brief malfunction in the autonomous nervous system. This is part of the nervous system that controls the autonomic functions such as the blood pressure and the heart rate.
First aid for fainting
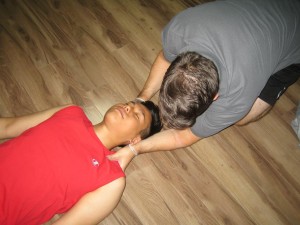
If an individual faint, he/she should lie down in a position where the head is low and the legs are elevated. This will promote the flow of blood to the brain.
In case it is not possible for the individual to lie down, he/she can rest with the head in between the knees.
Once an individual faints and does not regain consciousness in one or two minutes, you have to place him/her into the recovery position by:
- Placing on the side to be supported by one leg and one arm
- Open the airways by tilting the head back and lifting the chin
- Monitor the breathing and pulse rate continuously
Call for an ambulance and stay with the individual until the medical team arrives.
Treatment
In most instances, an individual is able to return to his/her normal state within a few minutes of fainting and no further treatment is needed. If an individual has repeated episodes of fainting, assessment by a doctor is needed to determine the cause.
The treatment for fainting depends on the type. If an individual experienced an episode, measures to deal with the future episodes include the following:
- Avoidance of triggers such as emotional stress, hot and crowded areas
- Determining the warning indications such as lightheadedness
- Lying down to increase the flow of blood to the brain
Quick Note / Disclaimer
The material posted on this page on fainting is for learning and educational purposes only. To learn to manage fainting, register for a first aid and CPR course with Saskatoon First Aid.
